
Unlock the Power of the Platform for managing Cisco networks
Do you feel like your efforts to simplify network operations are being outpaced by growing network...
Step up to a future-ready network.
Software-defined access (SD-Access) represents a transformative shift in how network architectures are conceived, designed, and managed. By enabling the creation of multiple virtual networks on top of a single physical network infrastructure, and building on the principles of intent-based networking, SD-Access addresses the challenges of network complexity, security, deployment and operations.
A bustling hub with multiple airlines and service providers all sharing the same physical network infrastructure.
Cisco SD-Access is more than just a virtual networking model. To grasp the significance of SD-Access, it’s essential to first understand the challenges of traditional networking models.
Three tiers and three layers. Sometimes these layers may be collapsed; the core navigation might be collapsed together.
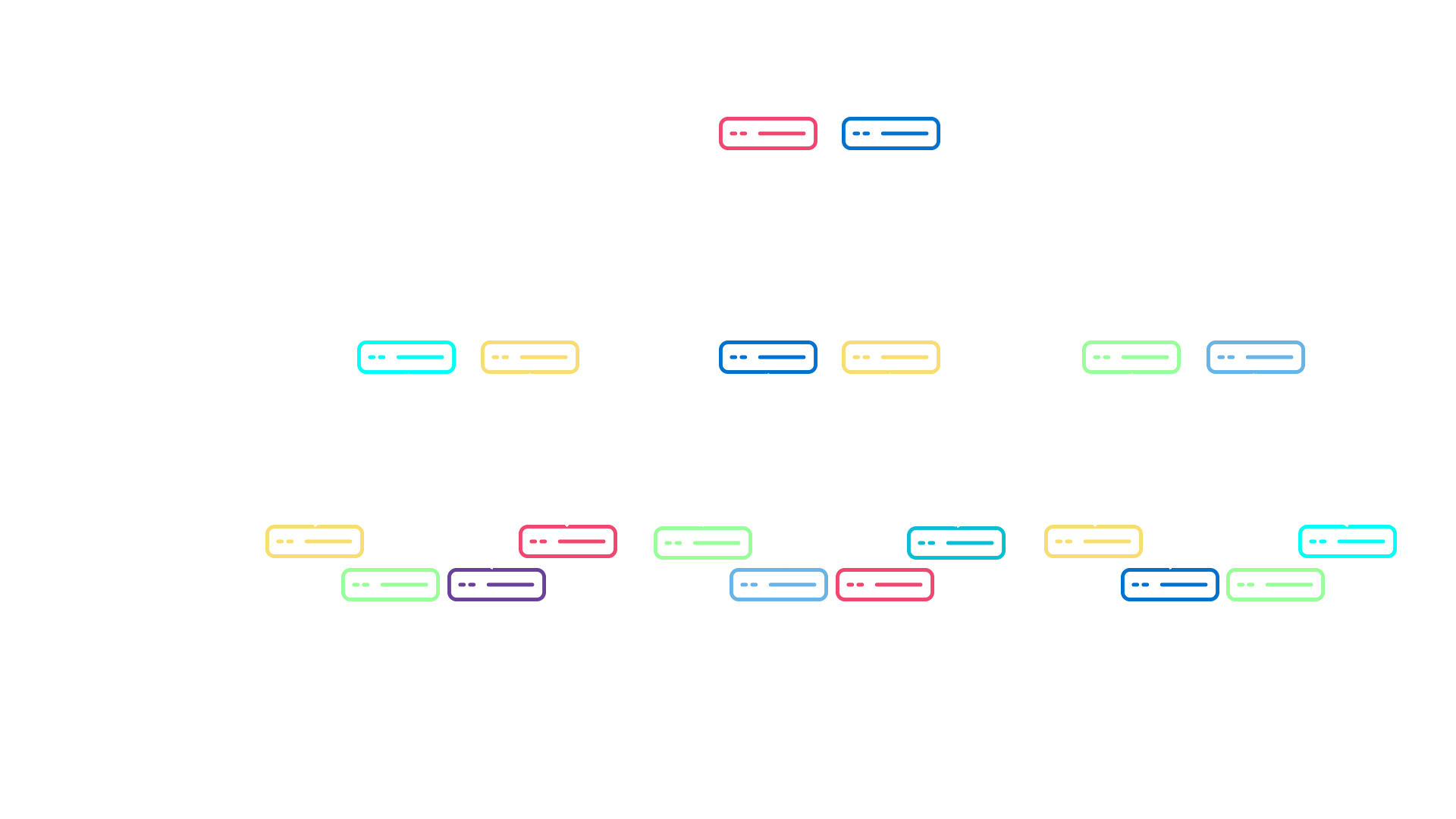
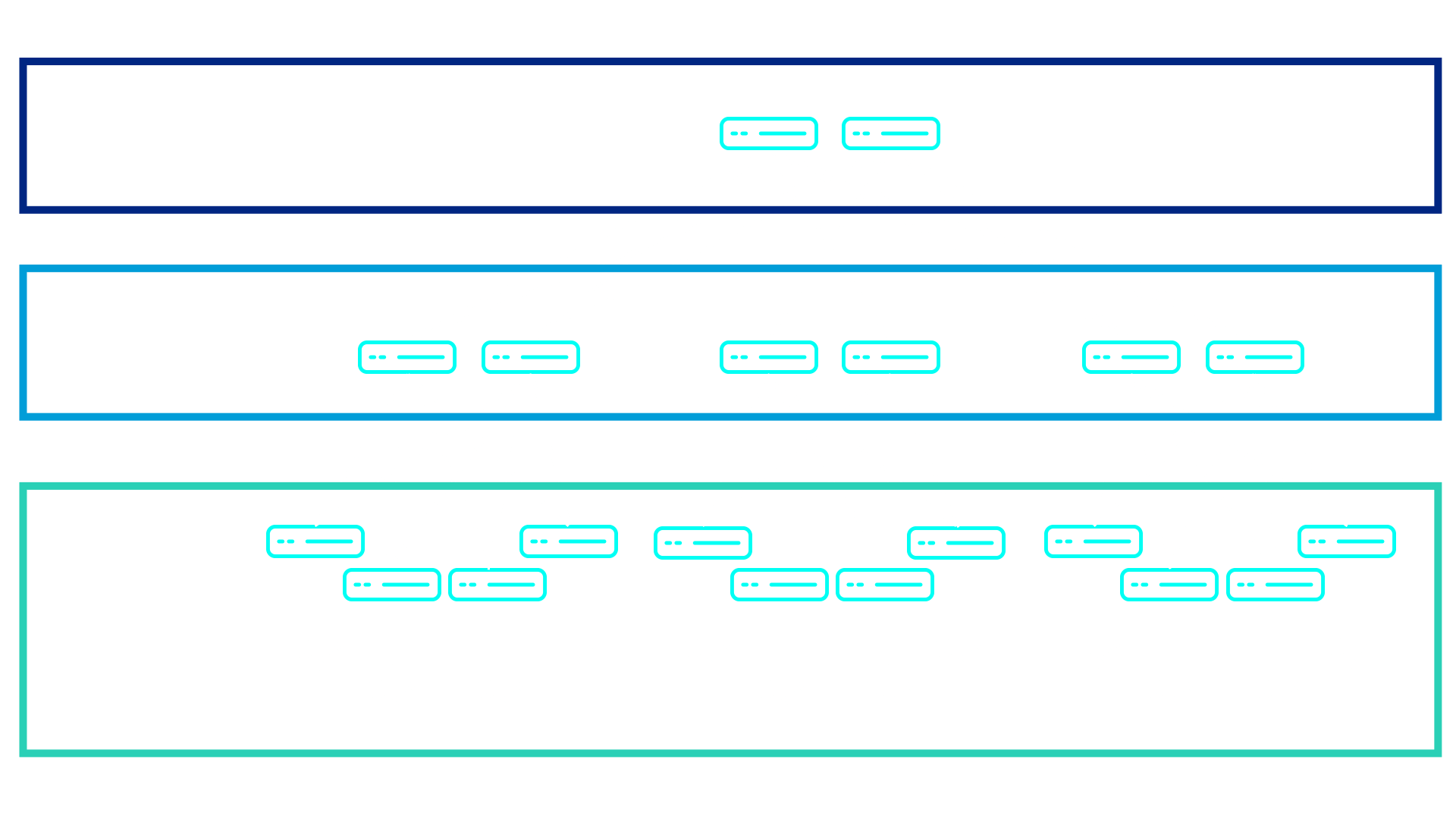
Over the years, networks have been configured with numerous network protocols, and this is where the problem lies.
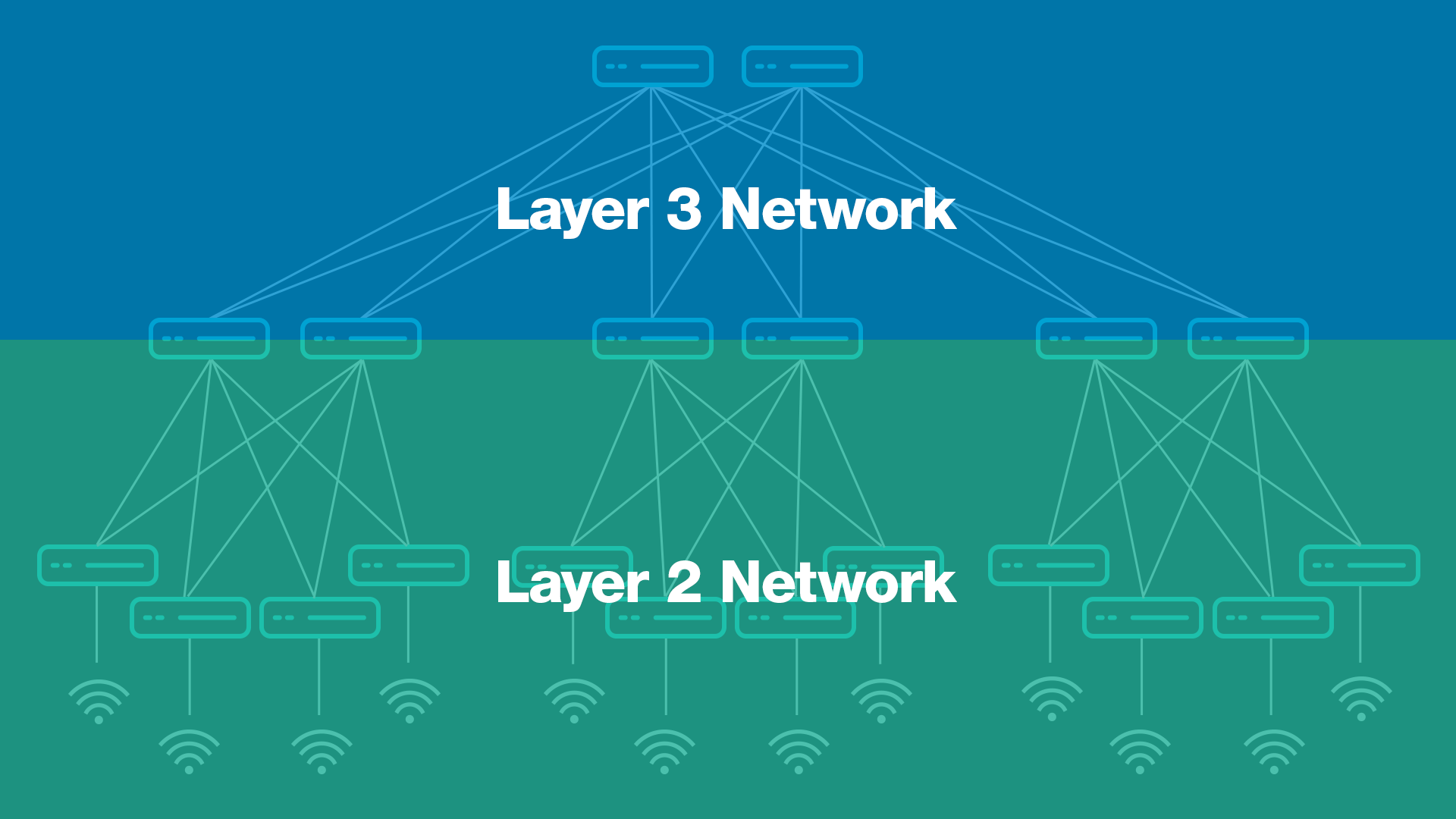
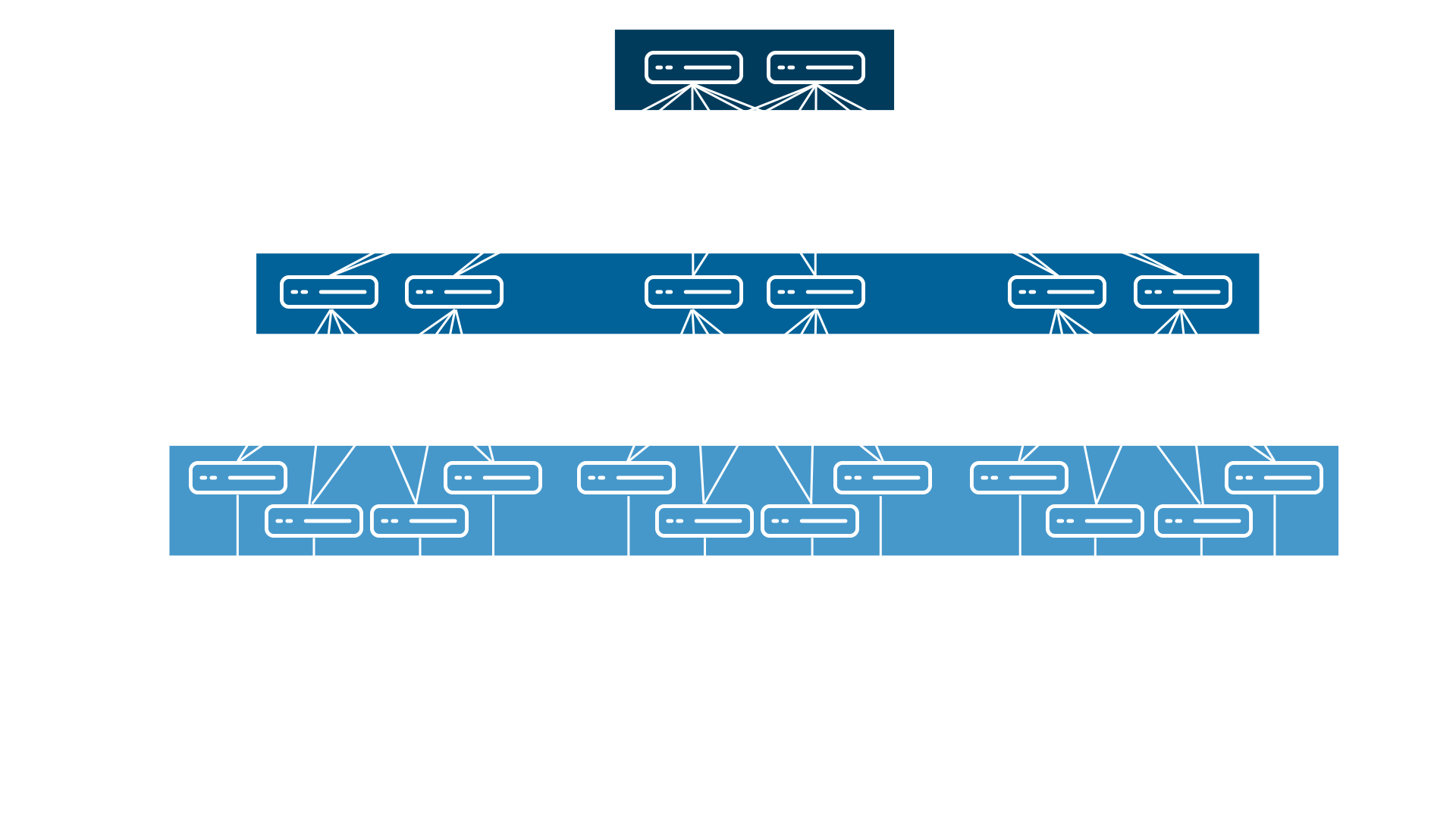
Cisco SD-Access provides quite a dramatic simplification, allowing you to shift from an old layer 3 network, separated by a layer 2 network approach, and make it a single layer 3 network where everything is layer 3 everywhere. This means fewer protocols and fewer configurations to manage.
Old enterprise network New enterprise network with SD-Access

Old enterprise protocol stack New enterprise protocol stack with SD-Access
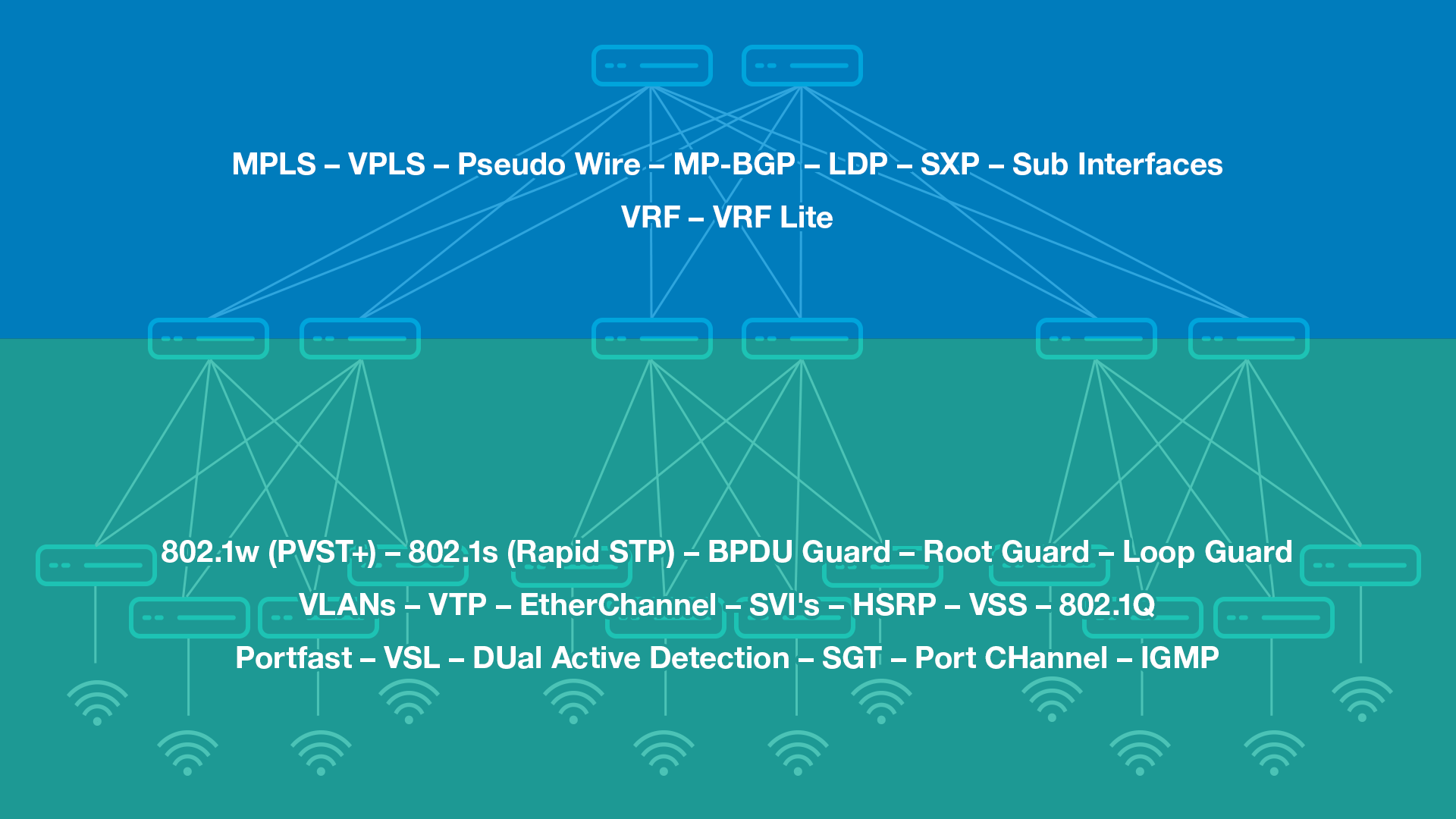
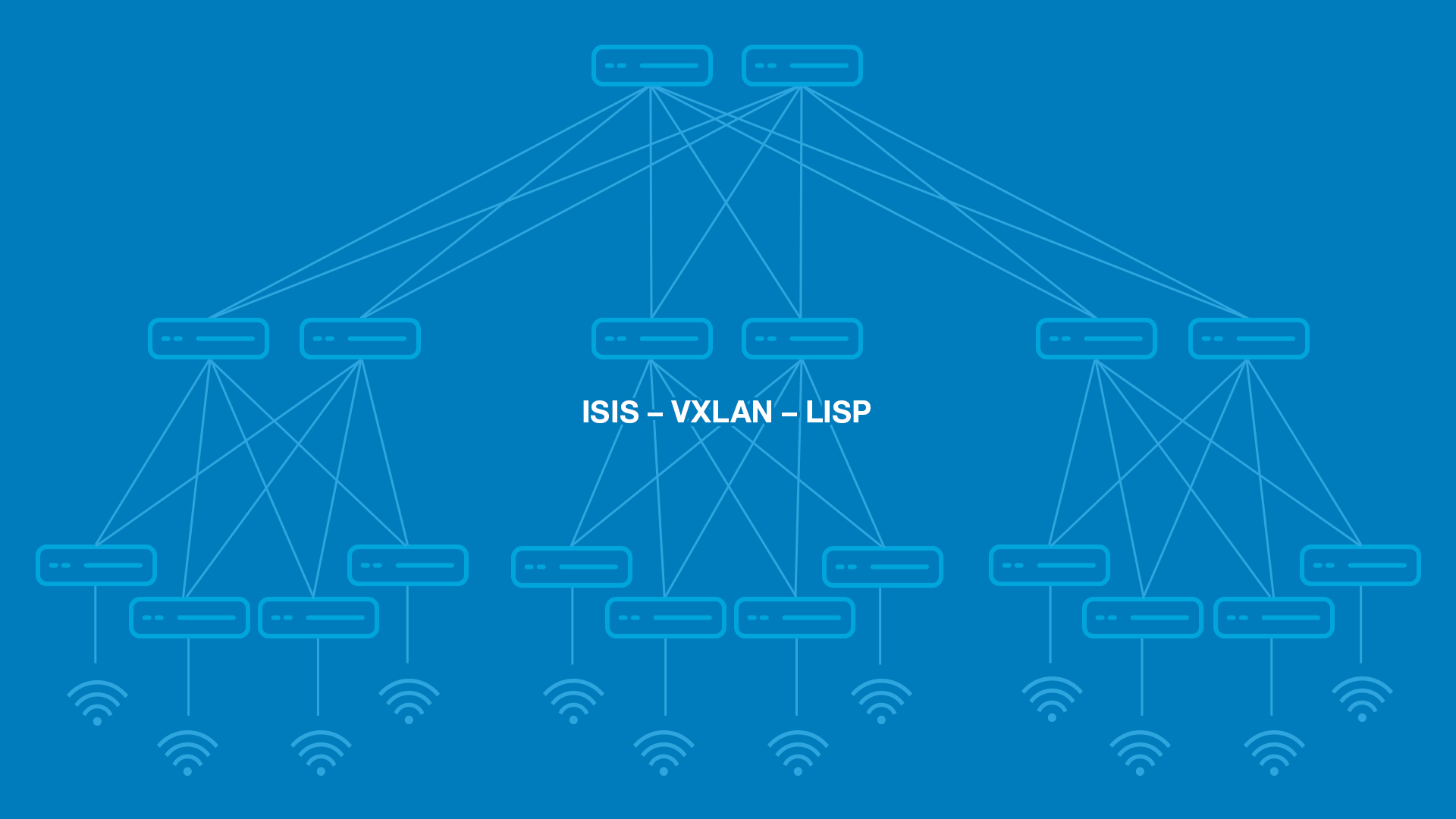
There is no longer a need for an in-depth understanding of intricate, low-level configurations because SD-Access takes care of many of these details behind the scenes. Rather than configuring each network device individually, policies and rules are inherited and automatically applied across the network.
Simplicity extends to policy enforcement where Cisco SD-Access introduces a unified approach for both wired and wireless networks. Rather than the wireless policies defined on wireless LAN controllers, and wired policies defined on the switches, SD-Access centralises policies on ISE (Cisco Identity Services Engine) for both wired and wireless users.
SD-Access decouples IP addresses from location, making it possible to apply consistent security policies across diverse locations, regardless of the underlying physical infrastructure. This is achieved through the use of Security Group Tags and their associated use cases rather than IP addresses.
Before SD-Access, customers had to rely on VRF or MPLS VPNs to segment and secure the network. This inevitably led to VPN/VRF sprawl and almost insurmountable challenges when attempting to introduce micro-segmentation.
With SD-Access, every device, user, or entity connecting to the network is properly authenticated, authorised and assessed by ISE before being automatically placed into their designated virtual network group and the right security policies applied.
When it comes to enforcing policy within the virtual network for micro-segmentation, Cisco SD-Access uses identity and ISE to dynamically assign policies and access rules based on user and device attributes – in tags, not IP addresses.
When devices connect to the wireless network they join a specific wireless controller. When they roam across the network from one AP to another, that roam goes back and is anchored against the original controller, and then it’s communicated to the other switches. This can result in duplicate MAC address errors and suboptimal roaming, and the wireless access controller acts as a choke point.
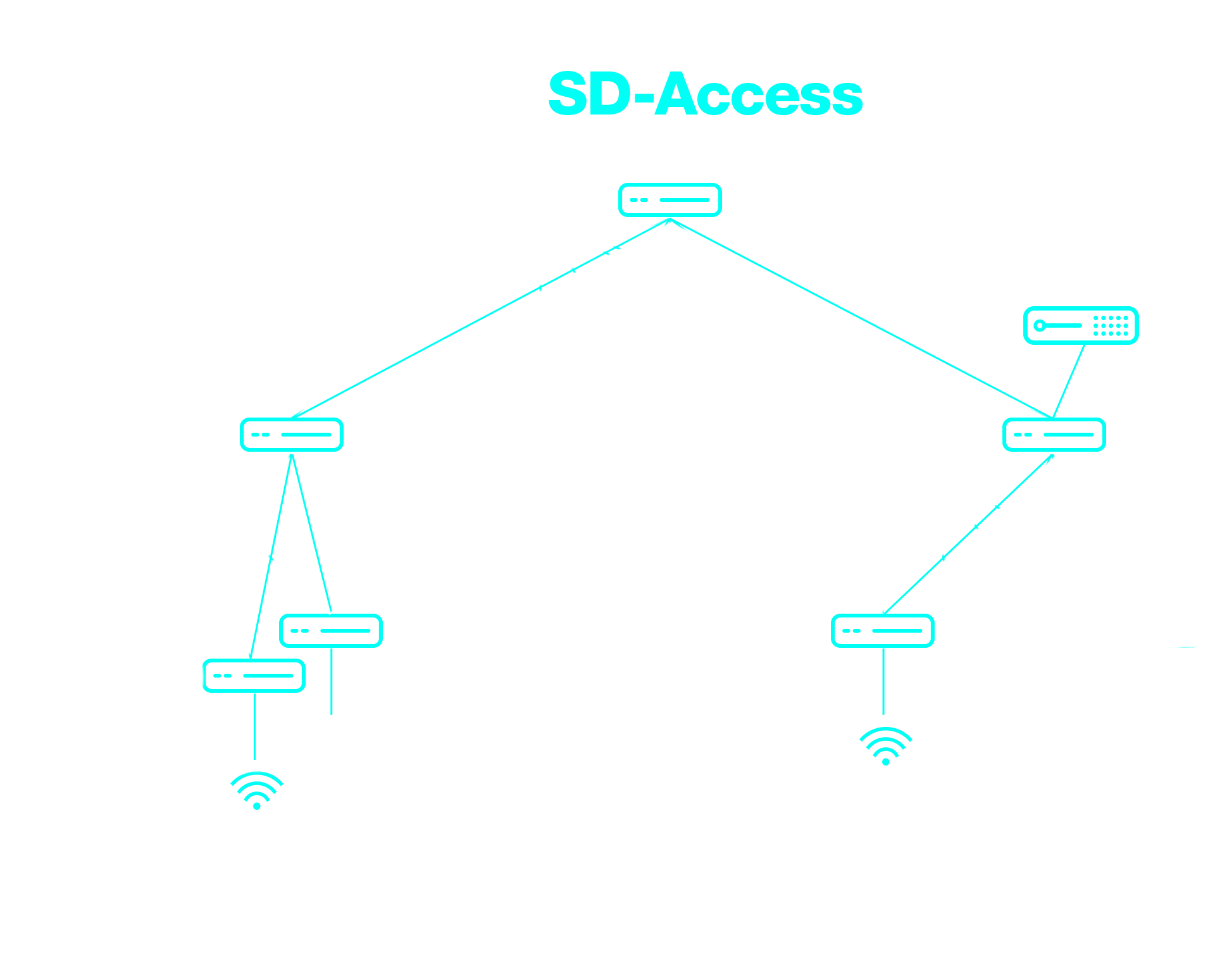
An overlay was required to facilitate mobility.
SD-Access takes a different approach by tunnelling traffic directly within the network fabric, eliminating the need for traffic to return to the Wireless LAN Controller. Instead, devices seamlessly connect to the network and communicate within the SD-Access fabric, enhancing scalability and performance.
SD-Access simplifies IoT device integration, treating these devices like users by employing MAC authentication bypass, certificates and device profiling methods to identify, authenticate, authorise and secure IoT devices. They are then placed in the right virtual network and isolated from the rest of the network without the need to use an 802.1x supplicant for authentication to the network.
It uses local device memory to track where hosts are located in the network.
Understanding the implications of SD-Access in your environment has become an imperative for network architects and administration teams. You don’t need to do this alone. Data#3 is a Cisco Master Specialised Networking Partner and 2023 Global Partner of the Year for Software. Let’s transform your network together – reach out to us today.


Do you feel like your efforts to simplify network operations are being outpaced by growing network...

We expect a lot from our networks – they must support hybrid work and cloud-centric models, stay on top...

The transformation of modern networks is an exciting, but challenging frontier in tech. It presents new...
As the complexity of network infrastructure escalates, intent-based networking is quickly becoming the...

While Cisco Prime Infrastructure was a reliable network management tool for its time, today’s network...

Earlier this year, I had the pleasure of attending the Data#3 Juice IT tradeshows across the country,...

Data#3 has won a $20.6 million contract to supply Cisco equipment and services to Main Roads WA...

The world you know is changing. The cloud is your new data centre, the internet is your new network,...

Enterprise architectures have fundamentally changed. Increasingly, the Internet is the new enterprise...

Digital Transformation at Qenos Delivers Substantial Business Efficiencies Project Objective Qenos sought...

Cisco ACI Solution Supports the Future of Business in Engineering Industry Objective When an ageing...

